The internal structure of the security camera
As mentioned in the previous chapter(Security camera classification), according to the different output video signals, we can divide security cameras into three categories: analog, digital, and network. Different types of cameras have different internal components and mechanisms, such as analog and digital cameras, which only have image processing and no video image encoding.
The internal structure and composition of the camera are introduced here for the sake of simplicity. On the whole, we can divide the interior of the security camera into three major parts: image capture, video image processing and coding, and signal output .
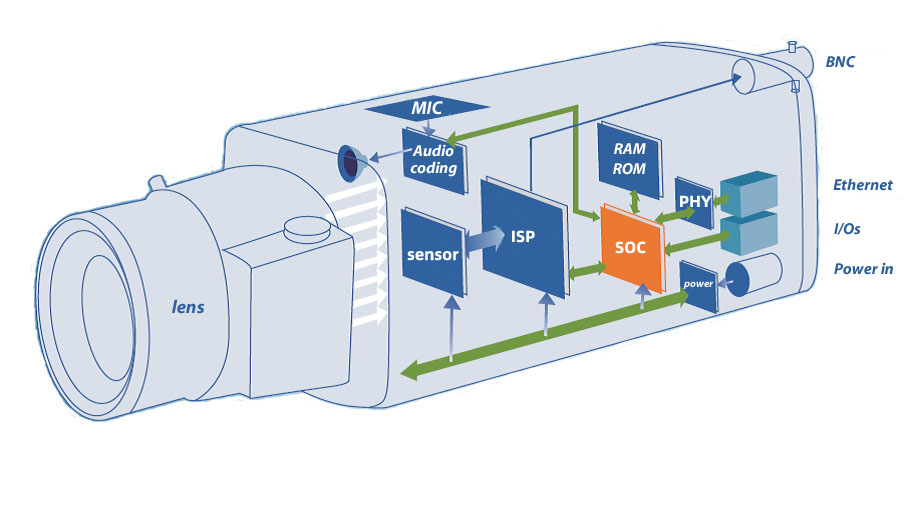
Image capture
The image acquisition of the camera is mainly completed by the lens and the image sensor on the chip. The light passes through the lens and enters the sensor on the chip. The sensor is responsible for converting the received optical signal into an electrical signal, and then handing it over to the subsequent unit on the chip for processing.
For video capture, please refer to Video parameters in security cameras.
The focal length of the lens (fixed focus, zoom), aperture, quantity (multi-lens used in multi-eye cameras), effective pixels, etc. will affect the signal sent to the sensor, thereby affecting the final imaging effect.
For the related concepts of the lens and its specific application in the security industry, please refer to the following chapters: Lens of security camera, Fisheye lens, Depth of field of Security video camera, and Camera selection based on pixel density.
After the light reaches the sensor, it first performs the preliminary processing of converting the light signal into an electrical signal. The main performance parameters of sensor include target size, effective pixels, low-light performance and so on. These will also affect the final imaging effect. For the parameters and performance of the sensor, please refer to Security image sensor, Starvis full-color camera technology, Wide dynamic function of security camera and other chapters.
Image processing, video coding
The electrical signal converted by the sensor needs to be delivered to the processor on the camera chip for image processing, video encoding and other operations.
The processor is a very general term, similar to the CPU of a computer or mobile phone. For cameras that output analog or digital signals, the processor here mainly refers to ISP, that is, Image Signal Processor.
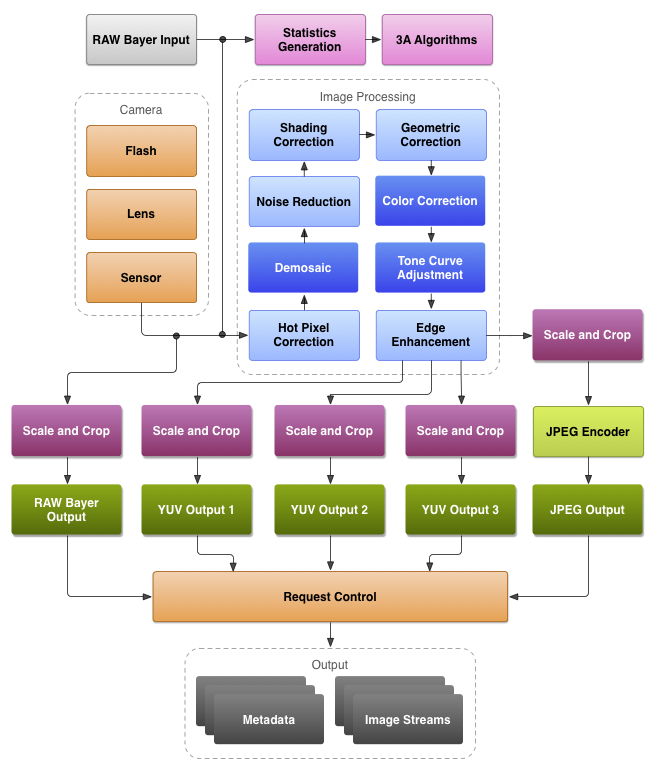
The main work of ISP includes:
- DEMOSAIC, translated into Chinese is anti-mosaic. Each pixel signal output by the sensor contains only one color data among R, G, and B. This kind of data is bayer data, which is commonly referred to as RAW data. Obviously, the color information reflected in RAW data is not true color information. DEMOSAIC’s job is to calculate the true color represented by each pixel through an interpolation algorithm, that is, to convert the Bell image into a true color image.
- 3A control. It is a collective term for Auto Focus (AF), Auto Exposure (AE) and Auto White Balance (AWB). This is the core part of ISP comparison, and the quality of processing is directly related to the final output image effect. ISP can realize auto-focusing through various auto-focusing algorithms such as CONTRAST AF, PDAF, LASER AF, etc., so that the target can be clearly imaged on the sensor. Exposure mainly affects the brightness of the image. ISP can control the degree of exposure to make the image brightness appropriate. White balance is related to color temperature and is used to measure the color authenticity and accuracy of an image. The automatic white balance function strives to accurately restore the original color of the target in various complex scenes.
- Gamma correction. The response of the sensor to light is different from the response of the human eye to light. Gamma correction is to make the image look in line with the characteristics of the human eye.
- Image cropping. That is, changing the size of the image can be used to output images of different resolutions. For example, the original resolution of 2048*1536, 4:3 is cropped to 2304×1296, and the resolution of 16:9 is more in line with the widescreen visual effect. Or a 5MP sensor, and it can also support different resolutions such as 4MP, 3MP, and 1080P.
- Intelligent Algorithm. Used to identify specific targets, such as face recognition, human shape recognition, license plate recognition, etc. ISP uses various intelligent algorithms to accurately identify specific targets. Of course, in the network camera, the intelligent algorithm can also be built into the encoding chip. At the same time, intelligent algorithms and structured data functions can be placed in the sensor. For example, Sony’s AI sensor (SONY IMX500/501) has achieved direct output of structured data.
- Dynamic Range. The dynamic range is the light and dark range of the image. ISP processing makes the dark part of the target image not under-exposed, and the bright scene is not over-exposed. In addition to the dynamic range processing supported by the ISP, the image sensor also needs to support the dynamic range (HDR) function. For details, please refer to the “Wide dynamic function of security camera” section.
- The image is stable and anti-shake. The main function is to prevent the image from being blurred due to the slight shaking of the camera.
In addition to the above work and processes, ISP’s functions also include noise reduction, contrast, saturation, sharpness, etc. Due to the technical accumulation of different manufacturers, different solution providers, and differences in algorithms, the image effects of cameras with exactly the same hardware solution will be different.
The analog optical signal is converted into a digital signal by the sensor, and after ISP processing, it can directly output the image of the digital signal, such as an SDI camera. It can also undergo digital-to-analog conversion again to convert the digital signal into an analog signal for output, such as analog SD cameras with traditional cvbs signals, and high-definition analog cameras such as AHD/CVI/TVI/XVI.
On the other hand, the digital signal can also be encoded and output and transmitted through the network, that is, a network camera. The encoding at this time requires a special encoding chip to complete. It should be noted that most of the current encoding chips have integrated ISP functions.
For processors with video encoding functions, we generally call them CPU, DSP or SOC. Strictly speaking, there is a difference between the three. But for the processing chip of a security camera, it is not bad to call it CPU, DSP or SOC. In order to unify and follow the manufacturer’s customary naming, we call the processors that support video encoding functions SOC.
SOC, or system on chip, can be regarded as a three-in-one processor, ISP, and encoding chip. The following is a block diagram of a typical security video encoding chip:

From this we can see that its main structure is divided into Quad Core Arm® Cortex®-A53 (ie processor), Image Signal Processor (ISP), Video Codec. The front end can be connected to sensor, audio, alarm and other equipment. In order to support the operation of the system, there are running memory and internal storage. It can directly extend WiFi/4G, SD card storage, etc., and can output analog/digital video, audio, alarm, network, serial port (485, 232) and other signals.
The core function of SOC is video encoding. For example, the typical SOC chip provided above supports three video encoding methods: H.264, H.265, and MJPEG. Related concepts of video coding have a detailed introduction about video coding in the section, so I won’t go into details here.
At this stage, with the development of chip technology and AI smart algorithms, more SOC manufacturers have built smart functions into SOC chips, which are more, more powerful and more scalable than those built into ISP.
Regarding SOC, DSP, that is, its intelligent functions, please refer to these chapters: Processors in security products-DSP, ISP, SOC.
Signal output
The video signal, audio or other signals processed by ISP or SOC can be output as analog, digital and network signals as required.
- Analog signal. After the electrical signal of the video image is processed by the ISP, it is converted into an analog signal by D/A and output through the BNC connector. Common analog video signals include standard definition CVBS, high definition AHD/TVI/CVI/XVI, etc. Theoretically, high-definition AHD/TVI/CVI/XVI signals can transmit audio, alarm, and control signals while transmitting video signals.
- Digital signal. After the electrical signal of the video image is processed by the ISP, the digital signal is no longer directly output through D/A conversion. The common output interface can be a BNC header or an HDMI interface. Such cameras are mainly SDI cameras. The HDMI interface can transmit audio while transmitting digital video signals.
- Internet signal. The digital signal is encoded by the encoding chip, and then can be transmitted through the network. This kind of network signal needs to go through the corresponding decoding to display the video image. Common decoding equipment and methods include the corresponding computer client, NVR, video decoder, network matrix, etc. On the other hand, audio, alarm, RS485 and other signals can also be encoded together with the video signal and then transmitted over the network.



Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!