5G
The development vision of 5G is to allow end users to always be connected to the Internet, that is, all things are connected. This should be the biggest feature of 5G compared to 3/4G. Faster speed and greater bandwidth are far less important than the interconnection of everything, especially for the Internet of Things and the Internet of Vehicles. Of course, 5G has little impact on the current development of the security field, and more of the future. When everything is interconnected, all security cameras can access the Internet quickly and at a high speed. There will be no dead angle in the whole world…
Development
5G (5th generation mobile networks or 5th generation wireless systems) is the latest generation of mobile communication technology, an extension of 4G (LTE-A, WiMAX-A) systems. The performance goals of 5G are high data rates, reduced latency, energy savings, cost reduction, increased system capacity, and large-scale device connections. The first phase of the 5G specification in Release-15 is to adapt to early commercial deployments. The second phase of Release-16 was completed in June 2020 and submitted to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) as a candidate for IMT-2020 technology. Release-17 is expected to be released in December 2021.
The ITU IMT-2020 specification requires a speed of up to 20 Gbit/s, which can achieve wide channel bandwidth and large-capacity MIMO. 3GPP will submit 5G NR as its 5G communication standard proposal. 5G NR can include low frequency (FR1), below 6 GHz and higher frequencies (FR2), above 24 GHz and millimeter wave ranges. In the early development, the speed and latency of using 5G NR software on 4G hardware (non-independent) were only about 25% to 50% improvement compared to the new generation 4G system. The simulation of independent eMBB deployment shows that the throughput is increased by 2.5 times in the FR1 range and nearly 20 times in the FR2 range.
Public information shows that Samsung was the first to start 5G research and development. At present, Ericsson, Intel, Huawei, and Qualcomm are involved in 5G research and development.
Advantage
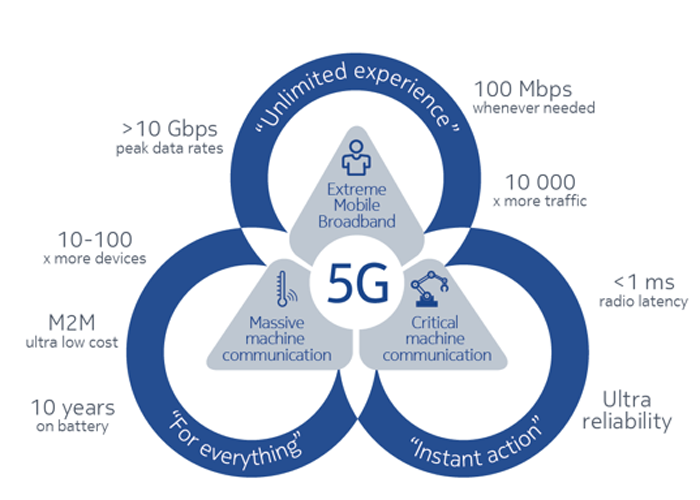
High capacity
Three times the existing spectrum resources, the number of connected devices increased from 105 to 106 per square kilometer, and the traffic density reached 10Mbps per square meter.
Low latency
The delay is reduced from 10ms to 1ms.
High speed
The transmission speed has risen from 1Gb/s to 20Gb/s, and the user experience data rate has reached 100Mbps.
High mobility
The mobility is up to 500 km/h.
Safety
Convenient
Energy saving
Energy efficiency is 100 times higher than IMT-A.
Low cost
Core application
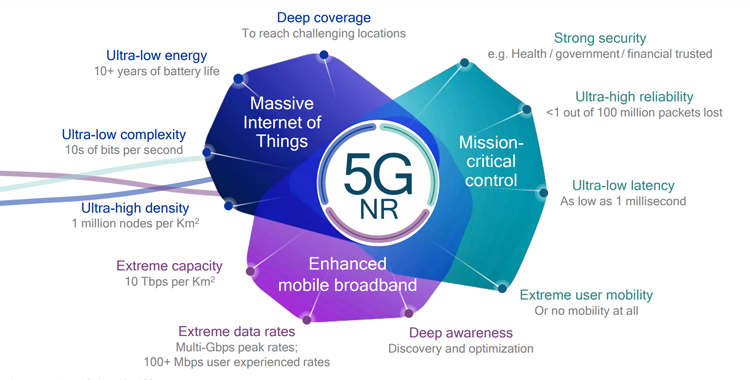
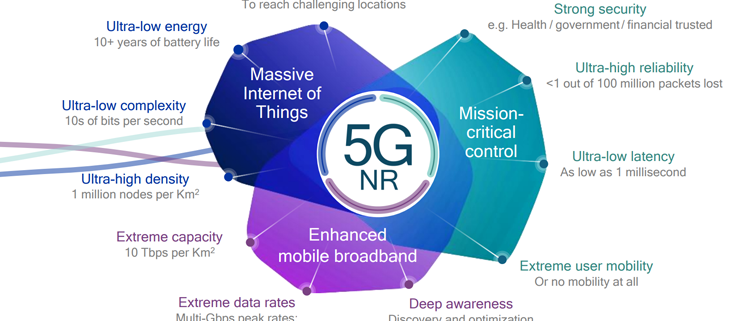
- eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband)
- mMTC (Massive MachineType Communication)
- URLLC(Ultra-reliableand Low Latency Communications)
Application field
- IOT
- AI/AR
- Mobile devices
Standard
3GPP formulated 5GNR, which was approved by ITU for implementation. Release-15 and Release-16 have been released Release-17 is expected to be released in December 2021. 5GNR is divided into independent networking SA and non-independent networking NSA two networking modes.
Frequency band
| BAND | FREQUENCY | TYPE |
| FR1 | 450 to 6000 MHz | Sub-6 GHz |
| FR2 | 24250 to 52600 MHz | mm-Wave |
SA,NSA
Independent networking (SA), introducing 5G base stations and 5G core networks in one step, does not rely on the existing 4G network, and has the shortest evolution path. The brand-new 5G base station and 5G core network can support all the new functions and new services introduced by the 5G network. The disadvantage is that the 5G frequency point is higher than that of LTE, and it is difficult to achieve continuous coverage in the initial deployment. There will be a large number of handovers between 5G and 4G systems, and the user experience is not good. The initial deployment cost is relatively high, and the existing 4G base station resources cannot be effectively utilized.
Non-independent networking (NSA), with the help of the current mature 4G network to expand 5G coverage. The NSA standard ends earlier and the products are more mature. Under the NSA network, there is no need to build a new core network, and the existing 4G core network will be used. The problem is that the 4G existing network must still be changed, the supplier structure of existing equipment cannot be adjusted, and the existing network cannot meet the requirements of 5G high reliability and low latency.
On the whole, NSA only supports eMBB services, and mMTC and URLLC services still need independent networking to achieve.
After 5G, 6G?
After 5G, there is 6(Number six chinese pronounced similar to english “no”) G? What needs to solve? If there is no need, there is no 6G.
Theory breakthrough,like Shannon theory.
Outlook: The frequency band uses terahertz, visible light frequency. The rate reaches the Tbps level, and the user experience rate reaches 10Gbps. The end-to-end delay is less than 1ms. Ultra-high mobility of 1000km/h. The packet loss rate is less than 10-8.
The impact of 5G on security
- 4G hardware costs are reduced, and LTE cat.1 and 5G develop in coordination.Thanks to the substantial reduction in the cost of 4G cat.1 modules, security manufacturers have recently launched a number of 4G security products.
- Networking of a huge number of surveillance cameras.
- Artificial intelligence, in-vehicle, wearable security equipment.
- Drone monitoring.
Problems applied in security
- Upstream bandwidth limitation.This is a regular question. The 5G network still has limited uplink bandwidth. The 5G network uses time-sharing transmission (different from the uplink and downlink full-duplex transmission of wired networks), 80% of the time is used to transmit downlink data, and 20% of the time is used to transmit uplink data, which means that the uplink in the 5G network Bandwidth accounts for only 20% of the total bandwidth, about 300Mbps, so the reality is not always so good. The large-scale use of 5G network transmission for video surveillance still seems undesirable, and further development of technology is needed. For example, ROI video coding technology, I frame optimization, network transmission optimization.
- 5G single base station has limited transmission distance and fast attenuation.As mentioned above, 5G transmission uses two bands of millimeter wave and Sub-6G, and the wavelength is relatively short, resulting in poor effective transmission distance, penetration and diffraction performance. Therefore, the standby capacity and transmission distance in a single base station are limited, and the installation location and number of cameras need to be considered.

5G related organizations, research institutions, enterprises
- 5g-berlin
- ITU
- 3GPP
- GSMA
- 5G Auto Union
- GTI
- NGMN
- 5G Networked Industry and Automation Alliance
- Linux Foundation
- Huawei 5G
- Samsung 5G
- Ericsson 5G
- Intel 5G
- Qualcomm 5G


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!